Risk vs return in investing takes center stage with a crucial exploration of the delicate balance between the two. Delve into the intricate world of investment decisions and discover how to navigate the dynamic relationship between risk and reward.
Explore the nuances of risk and return, and unveil the strategies for optimizing investment outcomes in a volatile financial landscape.
Understanding Risk and Return: Risk Vs Return In Investing
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Risk_Feb_2020-01-66f3c5ffb3c040848f1708091fa40eb9.jpg?w=700)
Risk and return are two fundamental concepts in the world of investing. Let’s delve deeper into what each of these terms means and how they are interconnected.
Risk in Investing, Risk vs return in investing
Risk in investing refers to the potential for loss or volatility in the value of an investment. It is essential to understand that all investments come with some level of risk, and the key is to manage and mitigate this risk to achieve desired returns. Different types of investments carry varying levels of risk, with higher-risk investments typically offering the potential for higher returns.
Return in Investment
Return in investment, on the other hand, represents the gain or profit earned from an investment over a specific period. It is the reward that investors receive for taking on risk. Returns can come in the form of interest, dividends, capital gains, or a combination of these. Investors typically seek to maximize returns while balancing the level of risk they are willing to take.
Comparing Risk and Return
When it comes to investing, risk and return are closely intertwined. Generally, higher-risk investments have the potential for higher returns, but they also come with a greater chance of loss. Conversely, lower-risk investments offer more stability but may provide lower returns. It is crucial for investors to assess their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon to find the right balance between risk and return that aligns with their financial objectives.
Types of Risks in Investing

When it comes to investing, there are various types of risks that investors need to consider. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed investment decisions and managing potential losses. Let’s explore some of the key types of risks in investing and how they can impact investment returns.
Market Risk
Market risk, also known as systematic risk, refers to the risk of investments losing value due to factors affecting the overall market. This type of risk is beyond the control of individual investors and can be caused by economic conditions, geopolitical events, or changes in interest rates. For example, a global recession can lead to a decline in stock prices across various industries, impacting the value of a diversified investment portfolio.
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk of a borrower defaulting on their debt obligations, leading to potential losses for investors holding that debt. This risk is prevalent in bonds and other fixed-income securities, where the issuer may fail to make interest payments or repay the principal amount. For instance, if a company issues bonds and later declares bankruptcy, bondholders may face significant losses as the company fails to meet its financial obligations.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the risk of not being able to sell an investment quickly without significantly impacting its price. Investments with low liquidity may have wider bid-ask spreads, making it challenging for investors to exit their positions at desired prices. For example, investing in real estate properties can pose liquidity risk as it may take time to find a buyer willing to pay the desired price, especially during economic downturns.
Inflation Risk
Inflation risk, also known as purchasing power risk, is the risk that the returns on investments may not keep pace with the rate of inflation. As prices rise over time, the purchasing power of money decreases, leading to a decrease in the real value of investment returns. For instance, investing in assets with fixed returns, such as savings accounts or bonds, may not provide adequate returns to offset the impact of inflation, resulting in a loss of purchasing power over time.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk refers to the risk that changes in interest rates can impact the value of fixed-income securities. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds with lower yields decreases, as investors seek higher returns from newly issued bonds. Conversely, when interest rates fall, bond prices tend to rise, benefiting investors holding these securities. For example, if an investor holds long-term bonds and interest rates increase, the market value of those bonds may decline, resulting in potential capital losses.
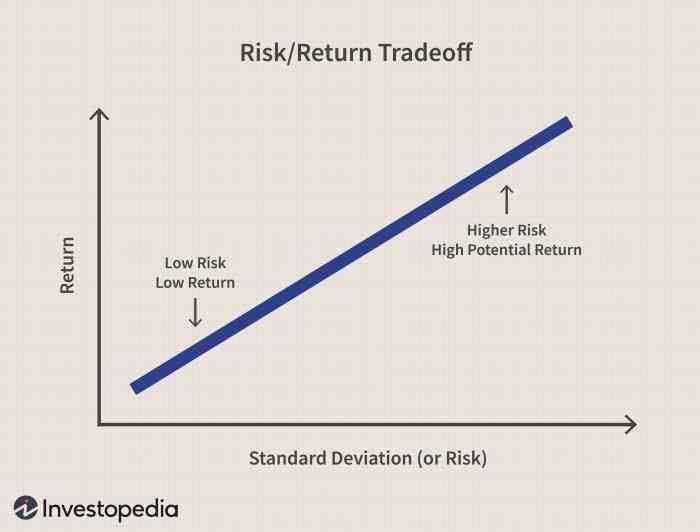
Risk-Return Tradeoff
When it comes to investing, the risk-return tradeoff is a fundamental concept that every investor should understand. This concept highlights the relationship between the level of risk associated with an investment and the potential return or reward that investors can expect to receive.
Higher risks in investing are often associated with the potential for higher returns. This means that investments with greater risk have the potential for greater rewards, but they also come with a higher chance of losses. For example, investing in high-risk assets such as stocks of emerging companies or cryptocurrency can result in significant returns, but there is also a higher likelihood of losing money compared to investing in safer assets like government bonds.
To find the right balance between risk and return based on their investment goals, investors need to consider their risk tolerance, investment timeline, and financial objectives. Some investors may be willing to take on more risk in exchange for the potential of higher returns, while others may prioritize capital preservation and opt for lower-risk investments with lower potential returns.
Ultimately, understanding the risk-return tradeoff is essential for investors to make informed decisions and build a well-diversified investment portfolio that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Diversification and Risk Management

Diversification is a risk management strategy that involves spreading your investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce the overall risk of your portfolio. By diversifying, you can potentially lower the impact of a single investment’s poor performance on your entire portfolio.
Strategies for Effective Diversification
- Invest in different asset classes: Spread your investments across stocks, bonds, real estate, and other asset classes to reduce the risk associated with a particular asset class.
- Diversify within asset classes: Within each asset class, invest in a variety of securities to further reduce risk. For example, in stocks, invest in different industries and company sizes.
- Consider geographic diversification: Invest in companies or assets from different countries to reduce the risk associated with a single country’s economic or political conditions.
- Rebalance regularly: Periodically review and adjust your portfolio to maintain your desired level of diversification as market conditions change.
Benefits of Diversification
Diversification can help reduce overall risk in your investment portfolio without sacrificing returns. By spreading your investments across different assets, you are less exposed to the volatility of any single investment. While diversification does not guarantee profits or eliminate all risk, it can help you manage risk more effectively and potentially achieve a more stable return over the long term.
In conclusion, mastering the art of balancing risk and return is key to achieving financial success in the realm of investing. By understanding the intricacies of this relationship, investors can make informed decisions that align with their goals and aspirations.
When it comes to retirement savings options for self-employed individuals, there are several strategies to consider. From setting up a Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA to contributing to a Solo 401(k), it’s important to explore the best fit for your financial goals. Learn more about the various retirement savings options for self-employed individuals here.
When it comes to retirement savings options for self-employed individuals, it’s essential to consider various strategies that can help secure your financial future. One popular choice is setting up a Solo 401(k) plan, which allows you to contribute both as an employee and employer. Another option is a SEP IRA, offering high contribution limits and flexibility. Additionally, a SIMPLE IRA is a straightforward choice for small businesses.
Exploring these options can help you make informed decisions about your retirement savings. Learn more about retirement savings options for self-employed individuals to plan effectively for the future.